Meiosis: The Big Picture
With the simple counter example from the previous sections, we have seen the basics of using Meiosis. We saw how to use a renderer, how to create a component with meiosis.createComponent, and how to run the application with meiosis.run. We passed renderer, initialModel, and rootComponent to run. We passed view, receive, and ready to createComponent. Now, let's look at the all the properties that we can use when creating Meiosis components. We'll also see the sequence in which Meiosis calls each function.
Initial Flow
The diagram below shows every property that you can pass to meiosis.createComponent. Remember that every property is optional. The diagram also shows how every piece of a component is called when you first run your application with meiosis.run:
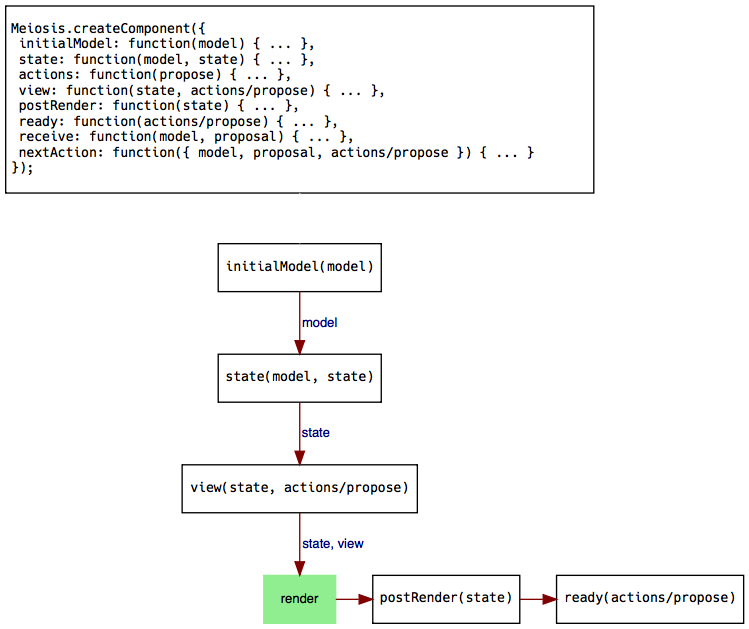
If you do not specify a particular property, skip that function in the diagram.
As you can see, this is what happens initially:
- The
initialModelis passed to thestatefunction. - The result of the
statefunction (application state) is passed to theview. If there is nostatefunction, theinitialModelis passed instead. - Meiosis also passes either the
actionsobject or theproposefunction to theviewfunction. - Meiosis passes the model or application state and the root component to the renderer. Specify the
renderer, theinitialModel, and therootComponentwhen calling themeiosis.runfunction. - If there is a
postRenderfunction, it gets called with the view. - If there is a
readyfunction, it gets called with theactionsobject or theproposefunction.
Propose/Receive Flow
After running your application, propose/receive are what make things happen. The following diagram illustrates what happens when you call propose from the view, an event handler, and so on:
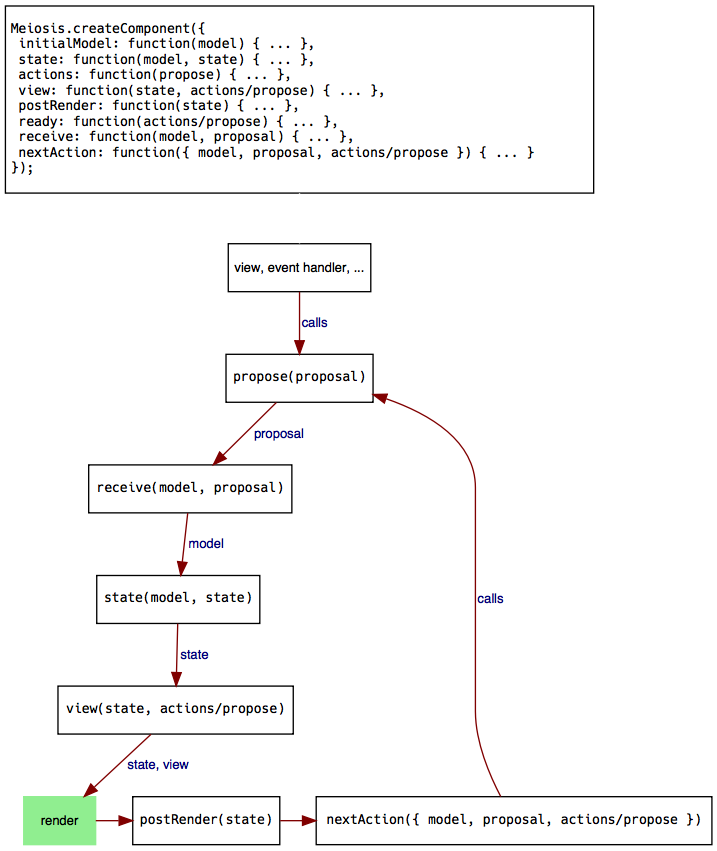
When you call propose:
- The proposal is passed to the
receivefunction. Meiosis also passes the latest model as the first parameter. - The model returned by the
receivefunction becomes the latest model. - The latest model is passed to the
statefunction. The result of thestatefunction (application state) is passed to theview. If there is nostatefunction, the lastest model is passed directly to theviewfunction. - Meiosis also passes the
actionsobject or theproposefunction to theviewfunction. - Meiosis passes the model and the root component to the renderer.
- If there is a
postRenderfunction, it gets called with the view. - If there is a
nextActionfunction, Meiosis calls it with the model, proposal, andactionsobject orproposefunction. ThenextActionfunction decides whether to trigger another action by callingpropose.
These diagrams are a cheat-sheet that you can return to for reference. In the following sections, we'll discuss each property that you can pass to meiosis.createComponent in more detail.